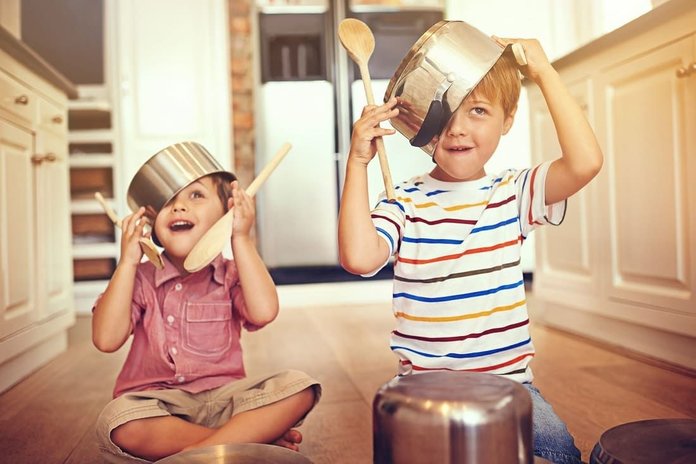
What if the child does not sit still: eats a spoon of porridge and runs away to toys, puts a cube on a cube and rushes on, cuts circle after circle in the clinic, and does not sit on a swing for a second in the playground? If a child cannot sit in class and play calm games - what is it: restless character or pathology of brain development? Whether the help of a specialist is needed or if this will pass over time is a matter of concern to many parents.
How to identify a hyperactive child?

Despite the fact that hyperactivity has many pronounced signs, it is not always possible to distinguish it from simple activity in many parents. The child does not have clear signs of hyperactivity, but there is a set of behavioral patterns that can indicate the presence of the syndrome.
First, it’s worth analyzing what the term “hyperactive” means.
ADHD or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder is a medical diagnosis that is usually made after a child is 4 years old.
Little children are always mobile, they actively explore the world, taste everything, touch, ask and look everywhere they can. To know the world is the first instinct of a growing organism. However, hyperactive children are not so much reaching for new knowledge as for emotions, exploring the world aimlessly, haphazardly, chaotically and uncontrollably. Their activity actually does not carry any cognitive meaning: jumping, racing, popping, jerking, cries and cues devoid of purpose. In this, not only is there no benefit to the development of children's minds, but there is also a huge danger to health and life in general.
The first and main symptom of ADHD, which manifests itself already at an early age, is excessive motor activity.
With a 95% probability, the presence of ADHD can be suspected if the child fits at least six out of seven common neurological signs:
- A hyperactive child quickly develops physically: before peers begins to sit down, crawl, stand on his feet and run. After some time, his movements begin to be dangerous: he falls off the sofas, drops furniture on himself, forever hits the corners and flips everything that is poorly set.
- When a hyperactive child gets tired, loses strength and wants to sleep, his activity seems to increase, and along with it the level of nervousness increases: he is naughty, nervous, whimpering, angry, and having difficulty falling asleep only after a long motion sickness in his mother's arms.
- At a young age, hyperactive children sleep abnormally little. While their peers spend at least half their days in sleep, children with ADHD can stay awake, play, and cry for more than 4-5 hours continuously.
- Such children fall asleep for a long time, demand that they be rocked and sleep very sensitively, and waking up from the slightest rustle with difficulty fall asleep again.
- The hyperactive child is excited by new emotions, people and impressions.However, along with enthusiasm, bursts of whims come and attempts to attract the attention of others, and the more there are, the more capricious the child.
- Often hyperactive children are attached to their mother and are frightened of strangers. They can hide from other people behind their mother and be jealous of her relatives and other children.
- They constantly switch their attention from one subject to another, not lingering on anything for a long time. New activities and toys capture them for a short while, after a short time, a hyperactive child loses interest in them and it is not possible to make him sit at the table.
These symptoms are not an unconditional confirmation of ADHD, but these are characteristic neurological manifestations that require immediate medical attention from a neurologist for detailed advice.
Causes

The exact causes of hyperactivity in children are still unknown, but numerous studies have brought modern medicine closer to the understanding that the roots of this syndrome go back to genetics and socio-psychological factors. So, ADHD cannot be called a disease and cannot be “cured” of it, since hyperactivity is not affected.
The most common common causes of hyperactivity disorder and attention deficit disorder are genetic malfunctions, congenital changes in the brain and socio-psychological factors.
ADHD can be caused by a number of reasons:
- Heredity. Studies of hyperactivity in twins led to conclusions about the genetic nature of the syndrome. According to WHO, the likelihood of inheriting ADHD is about 32%;
- The negative course of pregnancy and childbirth. In children of women over the age of 45, children with dyspraxia and signs of impaired attention are much more likely to give birth;
- Malnutrition during pregnancy, premature birth, low birth weight, painful toxicosis and the threat of termination of pregnancy are factors that can trigger the development of ADHD;
- Stress hormones, the mother’s anxiety during pregnancy can be transmitted to the fetus and also provoke a violation of its development;
- A negative family situation cannot be the cause of the development of ADHD, but it can contribute to this by reinforcing and reinforcing mental deviation, and in the case of a child’s genetic predisposition, constant stress can aggravate his condition to clinical;
- Parental abuse of alcohol, physical punishment, rudeness, intolerance, conflict, and a lack of parental readiness for children and family life can have a negative effect on the development of hyperactivity.
However, hyperactive children often appear in prosperous families, with a favorable course of pregnancy, childbirth and a general positive atmosphere for the family. In this case, it is worth talking about the genetic component of the disease.
Whatever the reasons for the development of ADHD in a child, this is not a sentence and you can cope with it if you act correctly.
Rules of conduct for parents

A lot of scientific articles and pedagogical books have been written about children with hyperactivity, however, the main work on raising perseverance and calm in children with ADHD takes place at home. Experts recommend that parents follow a series of actions that are aimed at gradually reducing unnecessary activity and channeling energy in a useful direction:
- Create a calm and quiet environment at home, without noise, loud noises, and especially swearing and scandals;
- Set a clear sleep mode that allows the child to get enough sleep;
- Ensure that the child does not overwork and does not lose self-control due to fatigue;
- Develop conscious braking in the child, talk with him about his actions and consequences before he is about to do something;
- Treat all the actions of the child with understanding and calm;
- To accustom the child to the daily regimen, preferably in accordance with the regimen of the day in the kindergarten, where the children clearly have time for waking up, walking, eating, having an afternoon nap, etc .;
- More often going out with a child on hiking, games, classes in circles;
- To play with the child in calm didactic games (lotto, mosaic, constructors) in order to teach the child to focus, and in sports and active games in order to switch energy to benefit;
- Use physical activity to control energy expenditure, but control child fatigue;
- Use the large format method. To draw with a child, gradually reducing the size of a sheet of paper - this will allow him to learn to concentrate;
- Encourage the child for all actions in which he needed to keep his attention;
- Do not skimp on the praise that is vital for nervous, excitable babies;
- Read with them any stories and tales before bedtime;
- Avoid large and noisy gatherings, meetings, both adults and children;
- Do not offer many toys during games at once, let him concentrate on only one at a time;
- Exclude aggression and tone increase from communication with the child;
- Do not lock yourself in, talk about the characteristics of the child with specialists, educators, competent people who can help you establish the educational process;
- To entrust the child with small household chores of a daily nature that he can perform, moreover, regularly;
- Keep a diary or a wall table with the child in order to note the success of the child in kindergarten and at home;
- Defining the framework of permitted behavior firmly, but not cruelly, avoiding uncompromising orders, but pointing the child to subordination - kindly and persistently;
- Try not to say the word "can not", and if it is said - do not cancel it;
- To find interesting activities that are easy for the child, and by encouraging them to increase the child’s self-confidence;
- Give your child as much time, attention and positive communication as possible, since his hyperactivity is often only a way to attract your attention.
Following these simple rules at first, you can significantly adjust the behavior of a hyperactive baby for the better.
When should I contact a specialist?

The first symptoms of hyperactivity appear as early as 2-3 years, but only a specialist can finally confirm it, and then most often by the age of four. Many parents, when they reach the age of four, delay the time of contacting a specialist until the child goes to school, which makes a gross mistake.
ADHD is most easily treated at an early age when the baby is malleable and his psyche is easily rebuilt. At school, a whole bunch of communication problems arise with peers and teachers, and the children's psyche is additionally subjected to great stress. Therefore, it is worth contacting a specialist when the child is 3-4 years old and in the presence of a number of main symptoms:
- Restlessness;
- Impulsiveness;
- Ignoring the rules of conduct in society and at home;
- Trouble sleeping;
- Delays in mental development.
A competent specialist (psychologist, psychiatrist or neurologist) can diagnose ADHD based on a series of tests, a parental survey and several brain scans. Most often, with this diagnosis, non-drug treatment, behavioral therapy or training are prescribed, but in some cases, medication can also be prescribed.
Hyperactivity Treatment

In the treatment of ADHD in Russia, nootropic drugs are used that affect the integrative activity of the brain. These drugs can calm a hyperactive child to improve his memory and concentration.
The nootropic and cerebroprotective drugs that help in the treatment of ADHD include:
- Encephabol;
- Cerebrolysin;
- Picamilon;
- Pantogam;
- Phenibut
- Instenon Nootropil;
- Gliatilin.
Cytomedines are among the new pharmacological discoveries in the field of sedatives for children with hyperactivity, whose task is to promote the development and functioning of brain cells, for example, koteksins, a sedative for children from 3 years.
Pantogam is another popular sedative for a child, which can be taken after it reaches the age of 2 years. Pantogam helps reduce activity and nerve spasms.
For the treatment of ADHD, anxiety disorders and headaches in adolescents, the herbal medicine Gelarium Hypericum is used, whose effect is similar to antidepressants and anxiolytics.
In the non-drug treatment of ADHD, transcranial micropolarization is used, in which a small electric charge is applied to the brain tissue, the task of which is to activate the functional reserves of the brain. TSMP has no complications and side effects; it is successfully used in the treatment of nervous and mental disorders in children and has an effective effect in 80% of cases: it improves the general condition, reduces hyperactivity, increases attention and quality of coordination, and alleviates anxiety.
In addition to medicines for the treatment of hyperactivity in young children of preschool age, doctors often recommend behavioral therapy, as it contributes to the rapid abandonment of medicines.
Children’s attention deficit hyperactivity disorder causes stress and despair in many parents, but it is treated quite simply if you act correctly, know how to handle and how to treat a hyperactive child.